This is a beginner-friendly guide to Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) and SERP features.
In my last article, ‘What is organic SEO,’ I discussed organic SEO in detail to help you get started with SEO. We went through what SEO is, why it is important, how SEO works, and how you can get started.
If you want to master SEO, the next step is understanding what SERPs are, their features, and how you can optimize your website for SERPs.
I’ll cover the following:
- What are SERPs?
- Why is understanding SERPs important for SEO?
- How to get your website to show up in SERPs?
Let’s get started right away.
What are SERPs?
The full form of the term “SERP” is Search Engine Results Page.
It is the webpage presented to you when you make a query on a search engine like Google, Bing, Yahoo, or DuckDuckGo. Each SERP can be different based on the search term, user’s settings, location, and browsing history.
The SERP you get when you search for Car Wash from Alabama will be different from the SERP you get when you search from Paris.
SERPs are also (kind of) personalized these days, but in a way that helps the most qualified and relevant businesses and websites better.
Types of results in a SERP
In general, you can see three types of results in a SERP.
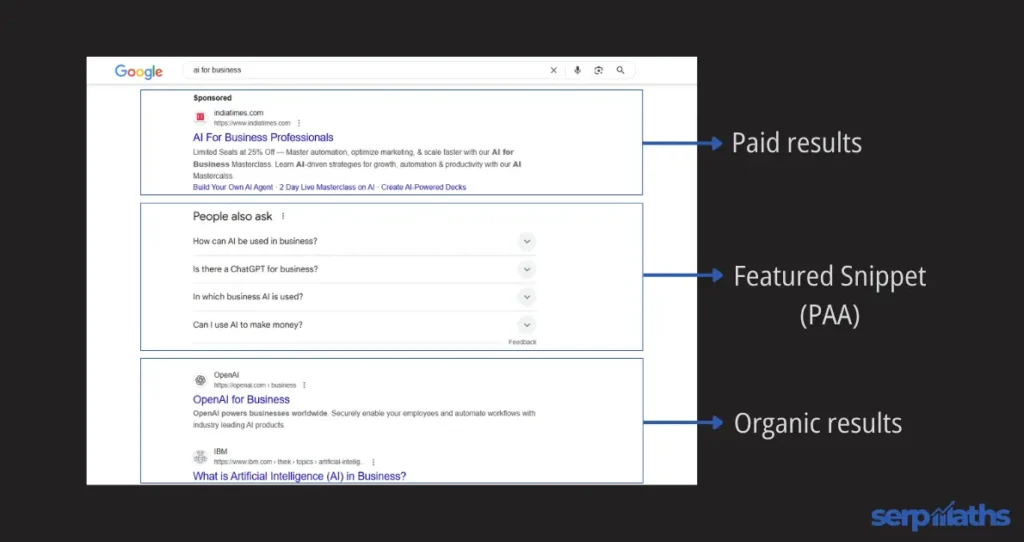
Paid search results
These results are sponsored by businesses—they pay the search engine to place their website in paid results. They are ranked based on how much they bid for each click.
Organic search results
These results are earned by each webpage, based primarily on the quality and relevancy of the content to the search term. Websites appear in organic results for free by following organic SEO best practices.
SERP features
SERP features are all types of search results other than paid and organic results.
There are several SERP feature results you’ll see on Google’s first page—from AI overview and featured snippets to direct answer boxes, knowledge graphs, local packs, and image packs.
I’ll briefly explain how you can get paid results, organic results, and featured results for your website later in this article.
Why is understanding SERPs important for SEO?
Organic search engine optimization (SEO) is basically the techniques and practices websites use to rank higher on SERPs to generate more traffic to the website.
The traffic from search engines is highly valuable as it helps businesses find new customers and make more sales. Search engine traffic converts better than other forms of traffic.
So there’s no SEO if there are no SERPs.
A whopping 39.8% of all clicks in the search results go to the top-ranked result in the SERP. The goal of SEO is to rank as high as possible, ideally at the number one spot or at least in the top three.
However, simply ranking in the top three doesn’t guarantee you massive traffic. Ranking for the right keyword with a good search volume is key.
And this is why understanding SERPs well is important for SEO—to make the most out of your efforts, you need to target the keywords that will generate decent traffic to your website if you rank at the top.
For instance, take the SERP for the keyword ‘Are PDFs bad for SEO?’
Google generates an AI overview and displays it at the top—it has all the details that a normal user would be looking for.
Someone who is just looking for a yes or no answer does not need to click on any search results now, as they have got the answer, and this impacts the CTR on other results.
In fact, a recent Semrush study has revealed that 25.6% of desktop and 17.3% of mobile searches are zero-click searches, partly due to SERP features.
When doing SEO, you want to target the keywords that can generate traffic and avoid the zero-click keywords. That ensures maximum returns on your SEO efforts.
How to get your website up on SERPs?
Since there are three types of SERP results, you can get into a SERP in three ways.
I’ll explain each one.
How to rank in Google’s paid search results?
Out of all three methods to get into SERPs, this is the quickest and easiest method if you have enough budget.
It can also be the most expensive.
Paid results or search ads do not show up for many keywords, but whenever they do, they show up above organic results on the first page of Google.
Depending on the query, search ads can also show up at the bottom of the page and even on the second SERP.
Search ads show up on around 35.82% of SERPs, mostly for commercial keywords. On Google, they usually have a ‘Sponsored’ tag. But according to a 2022 study, 68.2% of searchers don’t recognize Google search ads in SERPs.
Now, how do you make your website appear in paid results?
Setting up paid ads on Google is relatively simple. Go to Google Ads, add money to your account, select the keywords you want to show your website for, make a bid, and start running the campaign. That’s it.
Google search ads use a Pay-Per-Click (PPC) model. You pay Google every time your ad is clicked on.
You can bid on keywords of your choice—keywords related to your business or website. You’ll be competing with other businesses bidding for the same or similar keywords, and the highest bidders win.
Google will review your ad once you set it up, and if everything is all right, your ads will start showing up on Google. Your website gets traffic in no time.
On the other hand, the traffic from Google will become zero the moment your account balance drops to zero. Or when other businesses bid a higher amount per click for the keywords you were targeting.
How to rank in Google’s organic search results?
Organic results are those that show up on SERPs without having to pay Google. They are free listings.
Google uses a complex algorithm to decide which websites should be listed in organic results. Here’s a simple explanation of the mechanism:
Google employs bots called crawlers or spiders to go through the internet and collect information on webpages, such as what they’re about, how fast they load, how good is the user experience, how popular is the webpage, etc.
The information collected by the crawlers is added to Google’s database called the Search Index.
When a user makes a query, Google goes to its database and picks the most relevant and best-quality results to show on the SERPs. Here, the relevancy is determined by over 200 factors called ranking factors.
Businesses and web admins optimize their websites for these ranking factors. The process is called organic search engine optimization or SEO.
Now, not all of those 200 ranking factors are known because Google keeps them highly confidential, but the SEO community has identified some of them through experiments. The most important ones are:
- Quality and relevancy of the content
- Search intent—having the exact answer to what the searcher is looking for
- Links from other trusted websites pointing to your site
- Site loading speed, user-friendliness, visual stability, ease of navigation
- Overall user experience
The point is, in order to get your website up in organic results, you need to do SEO.
I’ve written a beginner-friendly article on organic SEO covering everything you need to know to get started. You can read that article to learn more about SEO.
Note that SEO takes time—at least a few months to show results. At the same time, apart from the initial investment in SEO to improve your website, you don’t pay anything to Google.
And once your website is up there in organic results, it can stay there for months or even years and keep generating traffic to your website.
All without paying a penny to anyone. And that’s why most businesses focus on SEO.
How to rank in the SERP Feature results?
Here’s a fact: nobody knows exactly how a website can rank in SERP feature results. Google chooses which result should have SERP features.
But we do know that providing enough information through Schema markups (structured data) is necessary for most feature results.
Schema markups are simple lines of code that help search engines understand your website content better.
If you are using WordPress as your CMS, you can use a plugin like Rank Math to add schema markups on all eligible pages and posts.
Otherwise, you can simply use standard schema markups on your pages.
For example, using the review schema on your review pages can get you a review snippet in SERPs. You must follow Google’s guidelines for review snippets to be eligible to feature as a rich result.
Similarly, using the FAQ schema for short-answer questions will make your site eligible to get an FAQ snippet in SERPs.
There are dozens of structured data types today, and it is important to use them to make the most out of the content you publish. You can use structured data for sitelinks, reviews, recipes, how-to guides, paywalled content, articles, courses, movies, books, etc.
Apart from getting you rich results in SERPs, structured data helps Google better understand your content.
And if Google finds your content the best one to feature in a SERP feature snippet, you will get a featured result.
Tools to analyze SERPs
Mangools SERP Checker
Mangools is an SEO tool that has many features of the standard all-in-one SEO tools, but their SERP checker is better than all other SERP analysis tools I’ve ever seen. It gives loads of data to make an informed, data-driven decision about keywords and content ideas.
Here’s what it returned when I used the SERP checker for the keyword ‘Steak recipe’:
It included data such as what percent of the result is visible above the fold, the average CTR, Domain Authority, Page Authority, Citation Flow, Trust Flow, no. of backlinks, referring domains, etc.
This is apart from the keyword difficulty and SERP features impact data. It also gives a snapshot of the first SERP in another tab.
However, it did not give more information on the SERP features the page had. It only displayed a ‘Similar Entities’ text above the first organic result. At the same time, the impact of the SERP feature was given as a number out of five, which is a valuable metric.
Ahrefs SERP checker
Ahrefs is one of the best SEO tools on the market. Their SERP checker did not have some of the features of the Mangools SERP checker, but it did show more information on the SERP features.
Here’s what Ahrefs SERP checker returned for the keyword ‘Steak recipe’:
It gives the Domain Rating, URL Rating, no. of backlinks, no. of referring domains, traffic, and the no. of keywords the website is ranking for.
It did not have the average CTR, visibility, keyword difficulty, or SERP features impact data like the Mangools SERP checker, which I find a little lacking.
At the same time, the SERP checker gave information on what kind of SERP features the page had and their placement in the SERP.
I have tried other tools like AccuRanker, SERP Watch, and WhatsMySERP, but they are all mere rank trackers or simply give a replica of the SERP with some DA-DR data, just like Ahrefs.
Honestly, except for the Mangools SERP checker, I think it’s better to simply use Google along with Moz chrome extension, Ahrefs chrome extension, and maybe Keyword Surfer—they give you more data than these tools do.
Search Engine Results Pages: FAQs
What does SERP stand for?
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Pages. It is the page you see after typing in a query into Google, Bing, Yahoo, or any other search engine.
What do SERPs include?
Search Engine Results Pages, or SERPs, include organic search results relevant to the user’s query. Depending on the query, SERPs may also include paid Google Ads results, Featured Snippets, Knowledge Graphs, Direct Answer Boxes, FAQs, and video results.
What are examples of SERPs?
An example of SERPs would be the Google results page when you type in the keyword ‘SERPs’ or any other keyword. Just like Google, all other search engines like Bing, Yahoo, Yandex, and DuckDuckGo also have their own SERPs.
Why are SERPs important?
SERPs are important since that’s where your website will appear if your SEO efforts become successful. Understanding the CTR and the popularity and authority of the websites currently ranking for your target keywords is important to ensure you get the most out of your SEO strategy.